Fragile X Syndrome (FXS) is a genetic condition that can cause learning, behavior, and developmental challenges, as well as various physical characteristics. It is the most common inherited cause of intellectual disability and is the leading known genetic cause of autism. FXS occurs when a change in the FMR1 gene on the X chromosome affects how the brain develops and functions.
While there is no cure, many people with Fragile X lead full, meaningful lives with the right combination of therapies, school supports, and medical care. Families often discover strength, resilience, and community through their journey. Here we explain and guide you through what Fragile X syndrome is, how it’s inherited, its signs and symptoms, and the treatments and resources that can help. We have several additional pages on the top topics within FXS.
A Guide for the Newly Diagnosed and Those Already Living with Fragile X
This guide helps answer common physical, cognitive, and behavioral questions. You’ll also learn:
— How Fragile X is inherited.
— Available treatment options.
— How females are affected vs. males.
— About the support you can receive from the NFXF.
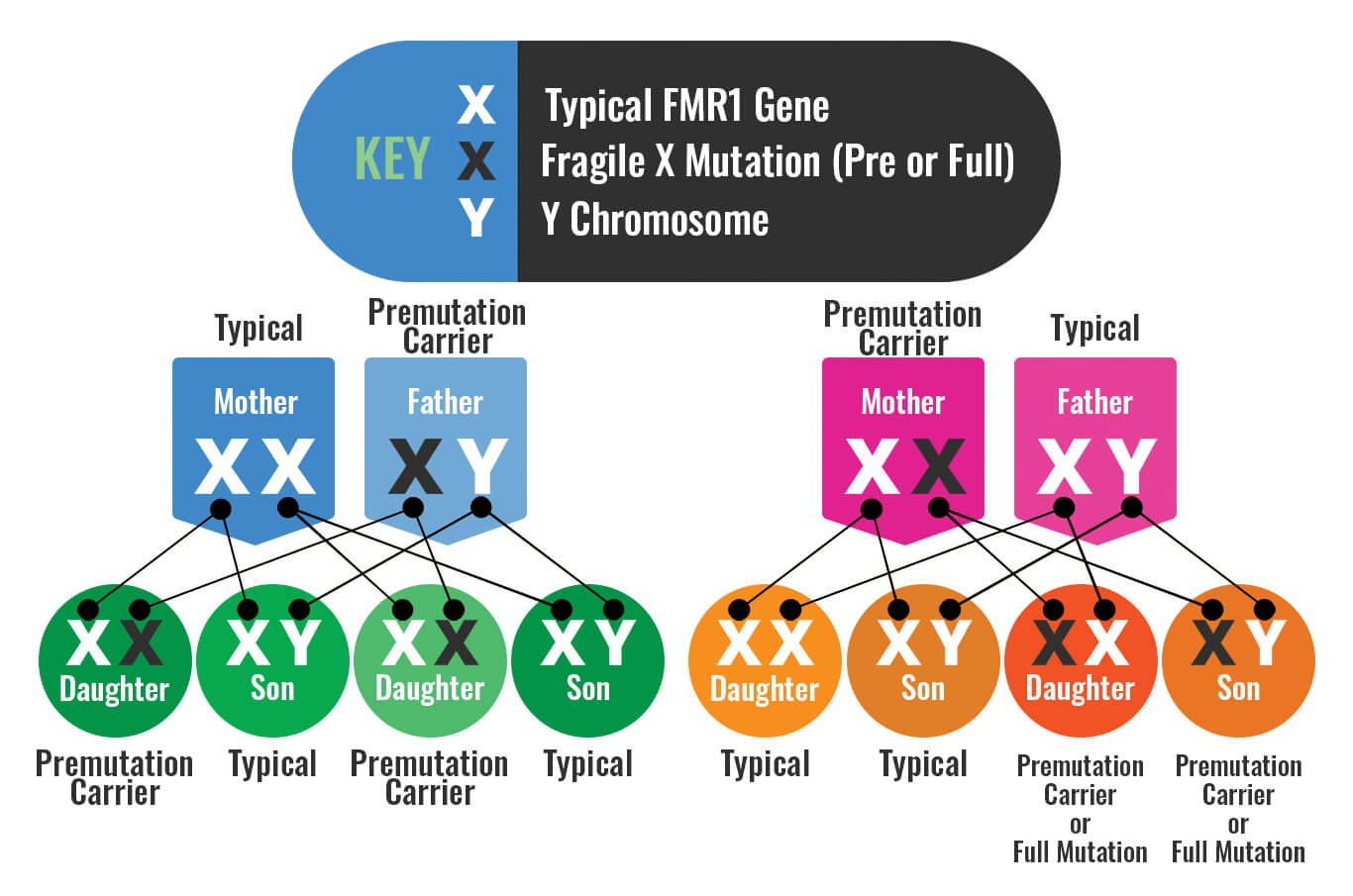
Females with the Fragile X premutation have a 50% chance of passing the mutation to each of their children, while males with the Fragile X premutation will pass it to all of their daughters (and none of their sons).
Fragile X syndrome occurs in both genders. FXS is more common in males than females, and males can experience more severe symptoms than females, though that is not always true.
Exactly why males are more often and more severely affected is unknown, but it’s believed to be because females have two X chromosomes and males have only one — can an impacted FMR1 gene on one X chromosome be compensated for by a typical FMR1 gene on the other? Because males have only one X, if they have an impacted FMR1 gene, it’s the only one they have. Females always have that second FMR1 gene, which may be able offset the effects of their impacted FMR1 gene.
The Prevalence of Fragile X Syndrome
FXS has been detected in all populations and ethnic groups. As a result, efforts have been made to determine the overall prevalence of FXS and the difference in prevalence between males and females. The current agreed upon prevalence of FXS from the CDC is ~1 in 7,000 males and ~1 in 11,000 females.

While researchers do not have an exact number for how many Americans could have full-mutation Fragile X syndrome, the ratios noted above suggest that the raw number of individuals could be as high as 87,000 or as low as 38,000. Worldwide, the number could be between 1,400,000 and 777,000.
It is important to note that some published papers suggest greater prevalence and some lower prevalence than the numbers cited above.
Why is Fragile X less frequent and less severe in females?
The reason there are fewer females with FXS than males is that the gene for FXS is located on the X chromosome. Males, having only one X chromosome (XY), will develop FXS because there is a mutation of their single X chromosome. Females, who have two X chromosomes (XX), can have the unaffected X reduce the effects of the affected X. This typically leads to no or milder symptoms of FXS. (This is an important distinction, as many females with the full mutation do not consider themselves, nor are they considered by others, to have “Fragile X syndrome.”)
Signs & Symptoms of Fragile X Syndrome
There are various signs and symptoms associated with FXS. No one individual will have all the features of FXS. The most common signs and symptoms include intellectual disability, behavioral and learning challenges, and various physical characteristics. These can be observed in both males and females with FXS, though there can be differences in how males and females present with FXS.
In Males
Behavioral characteristics can include ADHD, autism and autistic behaviors, social anxiety, hand-biting or flapping, poor eye contact, sensory disorders, sleep disorders, and increased risk for aggression.
Intellectual disabilities in FXS include a range from moderate learning disabilities to more severe intellectual disabilities. The majority of males with Fragile X syndrome demonstrate significant intellectual disability.
Other delays like speech, language, and motor delays (late crawling, walking, toileting) may also occur.
Physical features may include large ears, long face, soft skin, and large testicles (called “macroorchidism”) in post-pubertal males. Connective tissue problems may include ear infections, flat feet, high arched palate, double-jointed fingers, and hyper-flexible joints. Some features, such as a long face and macroorchidism, are more common after puberty.
Medical issues experienced by those with FXS may include strabismus (crossed eyes) and seizures.
Disposition in individuals with FXS includes being very social and friendly. They have excellent imitation skills, a strong visual and long term memory, they like to help others, and are nice, thoughtful people, with a wonderful sense of humor.

In Females
Behavioral characteristics seen in males can also be seen in females, though females often have a milder presentation of the syndrome’s behavioral, physical, and connective tissue features.
Intellectual disabilities in females with FXS range from none to significant. Severity of learning disabilities in females:
- About one third have none to very mild learning disabilities.
- About one third have mild learning disabilities.
- About one third have moderate to significant intellectual disabilities.
A small percentage of females who have the full mutation of the FMR1 gene that causes FXS will have no apparent signs of the condition — intellectual, behavioral, or physical. These females are often identified only after another family member has been diagnosed.
Additional challenges may include emotional and mental health issues, general anxiety, and social anxiety.
Language in Fragile X Syndrome
What does language development look like for individuals with FXS? We discuss receptive language (what is understood), expressive language (how an individual communicates), pragmatics (how language is used), and speech (how sounds and words are produced).
Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorder in Fragile X Syndrome
Clarification on how the ASD diagnosis and FXS do and do not overlap. Understanding this distinction can be particularly helpful for genetic counseling and deciding on the most appropriate interventions.
Sensory Processing and Integration Issues in Fragile X Syndrome
Sensory-based hyperarousal is the most prevalent, troubling, and defining characteristic in Fragile X. Learning to manage hyperarousal proactively allows people to grow into themselves, not out of the problem.
Sleep in Children With Fragile X Syndrome
Sleep problems can be more frequent in children with developmental disabilities, including Fragile X syndrome. Ongoing support can play an important role. Depending on the presentation and primary disorder, treatment may include behavioral, pharmaceutical, and surgical interventions.
Physical Problems in Fragile X Syndrome
Multiple associated physical problems can occur with FXS, mostly related to loose connective tissue.
Testing & Diagnosis
The FMR1 DNA Test (sometimes called the Fragile X DNA Test) is considered the standard of care for determining the presence of Fragile X. DNA testing detects more than 99% of individuals (both males and females) with FXS and the Fragile X premutation.
Genetics & Inheritance
Fragile X is passed down in families through a mutation in the FMR1 gene located on the X chromosome. Everyone has an FMR1 gene, the difference between having Fragile X and not having Fragile X comes down to CGG repeat number.
Fragile X-associated conditions include a wide range of physical, intellectual, and behavioral symptoms that can affect family members in many different ways. These conditions are passed down in families through expansions of the FMR1 gene.
FMR1 inheritance can be complex and confusing.
Treatment & Intervention
While there is currently no cure for FXS, there are treatments and interventions that can improve the lives of individuals living with FXS and their families. Many families choose a combination of treatment interventions that may include medications and non-medication-based treatments, behavioral and other interventions, and school supports. What works for one person may not work for another. With the right combination, all individuals with FXS can make progress!
Medication Treatments
There are Fragile X clinics across the United States and around the world. Clinics can guide parents to medication options that may address the symptoms of FXS while new medications that aim to treat the underlying condition are coming on the market. Individuals with FXS may also be prescribed medications that treat specific symptoms of FXS, like ADHD or anxiety.
Medications for Individuals with Fragile X Syndrome
Medications are, at times, helpful to facilitate the individual’s ability to attain optimal life skills and allow for better integration into educational, adult, and social environments.
Behavioral Treatments
Individuals with FXS may display behaviors—some good and some bad—just like everyone else. It is possible that you may encounter challenging behaviors. Challenging behaviors can be addressed by assessing the problem behavior and creating a plan that includes appropriate support and accommodations. These steps will likely foster positive outcomes and set up the individual with FXS to succeed in their home, school, or community.
Behavioral Challenges in Fragile X Syndrome
The most common behavioral challenges seen in FXS include those associated with generalized anxiety, social interaction difficulties, ADHD, self-injury, and aggression.
Educational Supports and Interventions
Most individuals with FXS qualify for special education services while in school. Education can be complemented by a variety of therapies that help individuals with FXS become more independent in the transitions from childhood through adolescence and into adulthood.
Learning does not end when school ends; the NFXF provides resources and tools to support individuals and their families through transitions from adolescence to adulthood.
Elementary School Educational Recommendations for Children with Fragile X Syndrome
Information on legal educational policies and recommendations, plus strategies and supports that have proven successful for academic and adaptive functioning.
General Educational Recommendations for Students with Fragile X Syndrome
A basic framework for understanding different aspects of the educational system and an overview of the terminology. We also have resources for each level of the education system.
Early Childhood Developmental and Educational Guidelines for Children with Fragile X Syndrome
For all children within the early childhood age range of birth to 5 years and especially for young children with identified disabilities associated with a diagnosis like Fragile X syndrome (FXS), inclusive, nurturing, and developmentally appropriate environments and caregiving are essential to growth and development.
Middle and High School Educational Recommendations for Children with Fragile X Syndrome
By using legal guidelines such as IDEA and implementing promising vocational, educational, and life skills training practices, students with FXS can be better prepared for a successful transition into adulthood.
Learn More About Fragile X Syndrome
Browse topics or visit one of the following: